Performing Arts
Welcome to the Performing Arts. Here you will find information about Drama, Dance and Music.
The Arts are central to Mayfield School: it is one of the golden threads running from the infants to the seniors. In Drama, we allow pupils to step outside of their comfort zone, step outside of themselves and learn to be confident, charismatic performers. Teaching pupils to embrace creativity and develop themselves as fully rounded people preparing them for their lives beyond school.
In the Infants pupils explore Drama through role play, each class has a role play area which allows pupils to engage their creativity in ever changing environments such as bookshops, post offices, and kitchens. Pupils begin to develop their story telling with the use of helicopter stories where they begin to perform vocally, beginning to understand and use prosody in their speech. Pupils build in their role play skills through the Jigsaw PSHE curriculum with specific role play scenarios. Pupils have an opportunity to perform to families in each year of infants to help build their confidence in performing, from year R Nativity to Red Hot Safari and Pirates V’s Mermaids.
In Juniors the skills learnt in infants are carried forward and developed to encourage a love of the performing. Pupils are encouraged to develop their speaking and listening skills through questioning, clarity of voice and improvisation of answers. Pupils develop their poetry skills through their English learning and perform these poems back to the class, developing their prosody skills. In KS2 pupils begin to learn about script writing and perform these scripts to the class, this gives them the understanding of transferring a script from the page to the stage. Juniors take part in performance opportunities form Matilda the musical to rainforest assemblies to develop their performance skills.
At Seniors we introduce a broad range of drama to give pupils a good base knowledge and understanding of the world of theatre. We continue to develop the key skills learnt in our primary section, and challenge these further still. Covering the key elements of making, performing and responding to drama, both scripted and devised. All key elements are introduced in our KS3 curriculum to ready pupils for KS4. The development of these skills over time is fundamental to success in drama. Pupils are introduced to a range of issue-based drama which helps them to consider their spiritual, moral, social and cultural development, with a focus on diversity. This is supported with the exploration of the GCSE exam stimuli which cover a range of areas.
All our work and effort in developing confident and talented performers culminates in the school production, a chance for pupils to tread the boards, stand under the lights and wear the greasepaint – experiencing the intoxicating thrill of a live performance. This could be a musical, like Our House, High School Musical, Into the Woods, or a play from the Shakespeare’s school festival to Brecht.
All the world is a stage, and we allow our pupils to be front and centre on it.
Spoken Language
Pupils should be able to;
-
listen and respond appropriately to adults and their peers
-
ask relevant questions to extend their understanding and knowledge
-
use relevant strategies to build their vocabulary
-
articulate and justify answers, arguments and opinions
-
give well-structured descriptions, explanations and narratives for different purposes, including for expressing feelings
-
maintain attention and participate actively in collaborative conversations, staying on topic and initiating and responding to comments
-
use spoken language to develop understanding through speculating, hypothesising, imagining and exploring ideas
-
speak audibly and fluently with an increasing command of Standard English
-
participate in discussions, presentations, performances, role play/improvisations and debates
-
gain, maintain and monitor the interest of the listener(s)
-
consider and evaluate different viewpoints, attending to and building on the contributions of others
-
select and use appropriate registers for effective communication
Spoken English
Pupils should be able to;
-
speak confidently and effectively, including through:
-
using Standard English confidently in a range of formal and informal contexts, including classroom discussion
-
giving short speeches and presentations, expressing their own ideas and keeping to the point
-
participating in formal debates and structured discussions, summarising and/or building on what has been said
-
improvising, rehearsing and performing play scripts and poetry in order to generate languages and discuss language use and meaning, using role, intonation, tone, volume, mood, silence, stillness and action to add impact
Dance; perform dances using advanced techniques and styles – PE national curriculum.
Spoken Language
The national curriculum for English reflects the importance of spoken language in pupils’ development across the whole curriculum - cognitively, socially and linguistically. Spoken language continues to underpin the development of pupils’ reading and writing during key stage 4 and teachers should therefore ensure pupils’ confidence and competence in this area continue to develop. Pupils should be taught to understand and use the conventions for discussion and debate, as well as continuing to develop their skills in working collaboratively with their peers to discuss reading, writing and speech across the curriculum.
Devising Drama
Learners should;
work collaboratively to create, develop, perform and evaluate their own piece of devised drama as either performers or designers.
Learner should know and understand;
-
research undertaken and how this has informed the development of the drama or design
-
how to develop an idea to progress from a simple to a more complex stage
-
how to plan, create and structure drama
-
how workshops can move the development of the performance forward
-
how to rehearse in preparation for a performance to an audience
-
how to make plans for the structure/form of an artefact – set, costume, lighting, sound
-
how to edit and adapt the work in progress as a result of new ideas or the development of the drama
-
how to examine in detail the process of creating drama and measure the impact on a live audience
-
how to communicate meaning to an audience through engaging drama.
Learners should be able to;
-
use research to inform creative decisions when devising their drama
-
examine the social, cultural or historical context of the chosen stimulus
-
explain how research has impacted on their artistic intentions
-
show the progression of their idea from initial thoughts to the realised form
-
select ideas to create engaging drama
-
clearly document the development of the performance during the devising process through the use of a portfolio
-
plan for effective use of rehearsals
-
refine and amend work throughout the devising process so that clear dramatic intentions are communicated to the audience
-
analyse and evaluate decisions and choices made during the process of creating drama
-
apply performance or design skills to performance for an audience
-
explain the changes made to their drama with reference to their artistic intentions and explain the intended impact on the audience
-
evaluate their final piece of devised drama
-
use accurate subject specific terminology
Presenting and Performing Texts
Learners Should;
-
study two extracts from one performance text
-
describe their artistic intentions for a performance
-
present two extracts in a showcase.
Learners should know and understand;
-
why the extract is significant in the context of the whole text
-
the structure of the whole text and the extracts’ place within it
-
the social, cultural or historical context of the text
-
the features of the text including:
-
genre
-
structure
-
character
-
form and style
-
dialogue
-
the role of stage directions
-
how to communicate effectively using:
-
the semiotics of drama
-
the skills of a performer or designer
-
performance conventions
-
how performance texts can be presented to an audience
-
the intention of the playwright
-
theatrical conventions
-
how to interpret character through voice, movement and language
-
the use of performance space
-
the semiotics of theatre as exemplified by the text studied
-
the relationship between performer and audience
-
how the different aspects of design impact on the whole creative experience for both performer and audience
-
the importance of rehearsal including time management and preparation.
Learner should be able to;
-
interpret the texts so that the playwright’s intention can be communicated
-
demonstrate the principles that will underpin their response to the key extracts through performance or design
-
apply their knowledge of genre, style and theatrical conventions to the way they will perform or design
-
use performance space effectively
-
develop a character or design and demonstrate the way it interacts with other characters or with stage artefacts
-
either: present a complete performance of the extracts with lines learnt, performance rehearsed and refined, performance skills used, intention of the playwright demonstrated and audience engaged
-
or: present a complete realised design for both extracts with final designs, artefacts, models or sets completed, as appropriate, intention of the playwright demonstrated and audience engaged
-
use rehearsals effectively to rehearse or make, and to adapt and refine their performance or design as appropriate.
Performance and Response; Written Exam
Section A
Learners should;
Study a whole performance text.
Learners should know and understand in relation to their performance text:
-
the contexts of their chosen text including:
-
social
-
historical (time set and period written)
-
cultural
-
the characteristics of their performance text including:
-
genres
-
structure
-
characters
-
form and style
-
theatrical setting (place)
-
plot and subplot
-
dialogue
-
stage directions
-
how meaning is communicated through:
-
the use of performance space and spatial relationships on stage
-
the relationship between performers and audience
-
the design of: set, props, costume, lighting and sound
-
an actor’s vocal and physical interpretation of character
-
the use of performance conventions.
Learners should be able to;
-
define how the social, historical and cultural contexts have an effect on the chosen performance text
-
explore and identify the characteristics of a text through practical preparation work and be able to explain the impact they have on a performance text
-
select examples from their own practical study which demonstrate knowledge and understanding of the full range of characteristics of the performance text
-
identify how a range of genres may have been used to inform the characteristics of the performance text
-
identify how meaning is communicated within the performance text
-
evaluate the roles that theatre makers (from contemporary professional practice) have on developing, performing and responding to a performance text.
Learners should in Section A: study the development of drama and performance.
-
contemporary staging including:
-
apron
-
black box
-
in the round
-
promenade
-
proscenium arch
-
site specific
-
thrust
-
traverse
-
the role of theatre makers in contemporary professional practice, including:
-
actors
-
choreographer
-
costume designer
-
director
-
lighting designer
-
lyricist
-
playwright
-
set designer
-
sound designer
-
stage managers
-
understudy
-
Acting skills including:
-
blocking
-
characterisation
-
improvisation
-
vocal techniques an actor might use to communicate a role
-
communication through physicality and the use of body language, facial expression and gesture
-
the use of semiotics
-
the design and use of a set including:
-
composite sets
-
non-naturalistic sets
-
the development of character through the creation and use of:
-
costume
-
hair and makeup
-
masks
Learners should be able to;
-
evaluate the roles that theatre makers (from contemporary professional practice) have on developing, performing and responding to a performance text
-
state advantages and disadvantages for the decisions made directing, acting and designing for a performance
-
apply knowledge and understanding of the development of drama and performance to the studied performance text
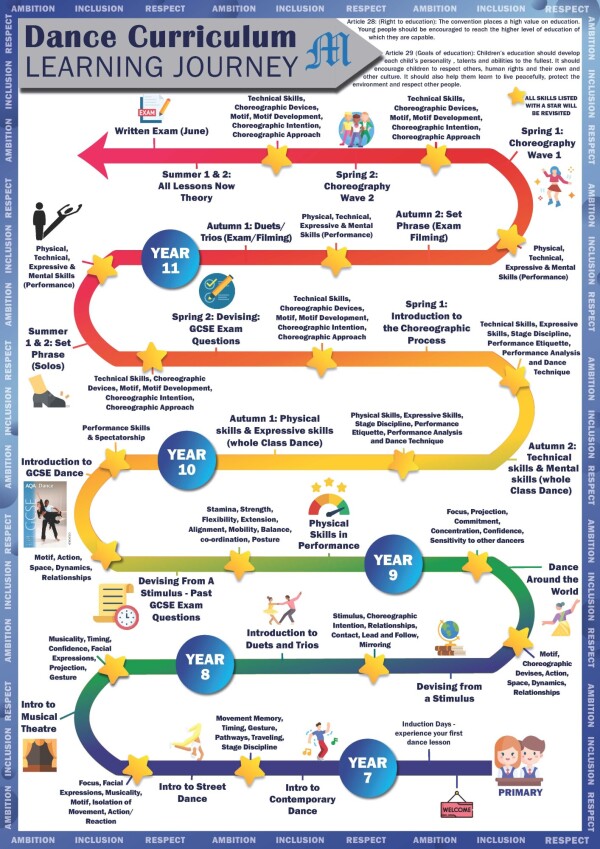
At Mayfield we are incredibly fortunate to be able to offer Dance as a highly valued subject in its own right. In KS1 & KS2 through their PE lessons our students will be introduced to learning and performing a range of movement patterns focusing on developing flexibility, strength, technique, control, and balance.
In year 7,8 and 9 all Mayfield students will have specific dance lessons where they will begin to develop their technique and improve their performance skills. They will learn and perform wide range of dance styles and techniques focusing on developing their understanding and analytical skills when self-evaluating, peer assessing and receiving constant verbal feedback from teachers- they will learn how they need to improve and will begin to apply this to their practical work whilst striving to achieve their personal best.
If a student chooses to carry on with Dance at GCSE level, they will develop their technique and understanding of a range of dance styles further. We focus on embedding a contemporary style within each dancer and a chance to find individual flare that can be applied in choreographic tasks and assessments. We encourage each student to find their style and inspire them to challenge, take risks and find the confidence to lead, choreograph and perform.
There are 3 practical elements that each student will complete:
-
Set phrases- 2 x 30 second phrases that are taught and performed to a metronome
-
Performance in a duet/trio- students will be grouped and taught some of the material for this performance- they will be given a chance to add individual flare and will be directed to make appropriate alterations to the choreography.
-
Choreography- students will learn the skills required to create their own successful choreography. They will lead a group of students and direct choreographic tasks accordingly in response to a given stimuli.
There is one written exam focusing on the following areas:
-
Section A- Knowledge and understanding of choreographic approaches and performing skills.
-
Section B- Critical appreciation of own work.
-
Section C- Critical appreciation of professional set works. Here they will study 6 professional work that range in theme, style, mood, and approach.
PE KS1 NC - perform dances using simple movement patterns
PE KS2 NC - develop flexibility, strength, technique, control and balance
perform dances using a range of movement patterns.
-
Develop their technique and improve their performance in other competitive sports
-
Perform dances using advanced dance techniques within a range of dance styles and forms- PE national curriculum.
Analyse their performances compared to previous ones and demonstrate improvement to achieve their personal best
|
Knowledge, Understanding and Skills for Choreography |
|
|
Action Content |
|
|
Dynamic Content |
|
|
Spatial Content |
|
|
Relationship Content |
|
|
Choreographic Process |
|
|
Structuring Devices |
|
|
Choreographic Devices |
|
|
Knowledge, Understanding and Skills for Choreography |
|
|
Aural Setting |
|
|
Performance Environment |
|
|
Communication of Choreographic intent |
|
|
Knowledge, Understanding and Skills for Performance |
|
|
Physical Skills |
|
|
Technical Skills |
Action Content E.g. -Travel, Turn, Elevation, Gesture, Stillness, Use of Different Body Parts, Floor Work, Transfer of Weight. Dynamic Content E.g. – Fast, Slow, Sudden, sustained, acceleration, deceleration, strong, light, direct, indirect, flowing, abrupt. Spatial Content E.g. – Pathways, Levels, Directions, Size of Movement, Patterns, Spatial Design. Relationship Content E.g., Lead and Follow, Mirroring, Action and Reaction, Accumulation, Complement and Contrast, Counterpoint, Contact, Formations.
|
|
Expressive Skills |
Communication of choreographic intent
|
|
Mental Skills (During Performance |
|
|
Safe Practice (During Performance) |
|
|
Mental Skills (During Process) |
|
|
Safe Practice (During Process) |
|
|
Knowledge, Understanding and Skills for Performance; Solo Performance |
|
|
Physical Skills |
|
|
Technical Skills |
Action Content E.g. -Travel, Turn, Elevation, Gesture, Stillness, Use of Different Body Parts, Floor Work, Transfer of Weight. Dynamic Content E.g. – Fast, Slow, Sudden, sustained, acceleration, deceleration, strong, light, direct, indirect, flowing, abrupt. Spatial Content E.g. – Pathways, Levels, Directions, Size of Movement, Patterns, Spatial Design.
|
|
Expressive Skills |
|
|
Mental Skills (During Performance |
|
|
Safe Practice (During Performance) |
|
|
Mental Skills (During Process) |
|
|
Safe Practice (During Process) |
|
Written Paper
|
Knowledge and Understanding of Critical Appreciation of OWN WORKS |
|
|
Performance |
|
|
Choreography |
|
|
Knowledge and Understanding of Critical Appreciation of SET WORKS |
|
|
Features of Production |
|
|
Performance Environment |
|
|
Choreographic Approaches |
|
|
Choreographic Intent |
|
The Arts are central to Mayfield School: it is one of the golden threads running from infants to seniors. Music is a universal language, one that speaks to every individual. At Mayfield, we give our pupils the opportunity to explore and develop their musical creativity from the earliest stage in the infants through to instrumental exams to show proficiency and advanced skill at seniors. We know that musical education and appreciation is central to the development of the whole person, as vital as imagination, as reading and writing.
We will create fully formed musicians, who are comfortable performing, composing and appreciating music in all its forms.
In Infants, pupils start their musical journey by becoming comfortable using their voices – principally by gathering together for a weekly singing assembly where they explore seasonal songs from traditional harvest festival music, to Christmas carols and modern, contemporary pop music. They also gain their first experience of instruments; beginning with percussion, including the djembe drums of Africa, through the ukulele and keyboards.
In Juniors, pupils get the chance to explore music individually – composing, performing and appreciating. They also get the opportunity to begin instrumental lessons - a range of instruments are available including voice, drums, guitars and keyboards. They continue to sing weekly as a group and deepen their understanding of instruments they have previously explored.
Our Primary section gets the opportunity to perform for each other, the school and a wider audience through events such as the nativity, carol concerts and the junior production - as well as celebration assemblies.
In Seniors, all pupils continue their appreciation of Music in Key Stage 3, developing their skills and knowledge, their ability with instruments and becoming more creative with their compositions and appreciation of the wider forms. Mayfield also encourages extracurricular expression through singing groups, like choir, to bands and the whole school production. Even the chance to record and share original and covered content with a wide audience. Upon reaching Key Stage 4, we offer a BTEC in Music, where participants are able to reach the highest grades.
Music teaches resilience, the ability to try and not be afraid, because the result will always be something interesting and a learning experience. In addition, Music is emotive and allows an expression of yourself unlike anything else. Above all, Music is what life sounds like and is the strongest form of magic.
Key Stage 1
Our students use their voices expressively and creatively by singing songs and speaking chants and rhymes. They play tuned and untuned instruments with increasing accuracy, developing musicality and technique. Students listen with concentration and understanding to a range of live and recorded music evolving their ability to respond aesthetically to music and identifying key musical features. Students experiment with and create, select and combine sounds using the interrelated dimensions of music to create pieces for desired effects.
Key Stage 2
Our students sing and play musically with increasing confidence and control. They develop an understanding of musical composition, organising and manipulating ideas within musical structures and reproducing sounds from a developing aural memory.
Students play and perform in solo and ensemble contexts, using their voices and playing musical instruments with increasing accuracy and expression.
They improvise and compose music for a range of purposes and desired effects. Students listen with attention to detail and recall sounds with increasing aural memory. They use and understand a range of musical notations including staff notation. Students appreciate and understand a wide range of recorded music drawn from different traditions and from great composers and musicians developing an understanding of the history of music
Students build on their previous knowledge and skills through performing, composing and listening. They develop their vocal and/or instrumental technique with increasing fluency, accuracy and expressiveness. Students understand musical structures, styles, genres and traditions, identifying the expressive use of musical elements. They listen with increasing discrimination and awareness to inform their practice as musicians. They learn to appreciate and understand a wide range of musical contexts and styles.
Students play and perform confidently in a range of solo and ensemble contexts using their voice, playing instruments musically, fluently and with accuracy and expression. We improvise and compose; extending and developing musical ideas by drawing on a range of musical structures, styles, genres and traditions. use staff and other relevant notations appropriately and accurately in a range of musical styles, genres and traditions. Students identify and use the Elements of Music expressively and with increasing complexity, including use of tonalities, different types of scales and other musical devices. They listen with increasing detail to a wide range of music from great composers and musicians understanding its context and history.
BTEC First Award in Music Levels 1/2
This qualification is comprised of 4 Units from these 5:-
1 The Music Industry Exam (1 hour)
2 Managing a Music Product
4 Introducing Music Composition (optional)
5 Introducing Music Performance
7 Introducing Music Sequencing (optional)
|
Unit1 – The Music Industry |
In this Unit we learn about different job roles and organisations that work in the Music Industry. In addition, we examine how the Music Industry works and how the job roles and organisations relate to each other. |
|
|
Unit 2 – Managing a Music Product |
This Unit enables students to manage the planning, delivery and promotion of a live concert. The students work as a team to plan, stage and perform in the concert. Each student is usually assigned a role to play in the planning stages individually and as part of a wider team, as well as contributing to meetings and performing in the actual concert. In addition to this each student is required to take part in the promotion of the concert and an evaluation of the concert to ascertain its successes and areas for improvement after the concert has been staged. |
|
|
Unit 4 - Composing |
This Unit offers the chance for students to develop their composing skills. They develop a portfolio of ideas and develop some of them into completed compositions. Students will study a range of compositional techniques and produce contrasting musical ideas to develop compositional skills. Briefs will be used to present students with real life composing challenges. E.g. Music for an advert or music for a film scene. |
|
|
Unit 5 - Performing |
In this Unit, students explore skills and make decisions as they prepare for a performance. Students are taught the importance of planning and rehearsal. They set themselves medium- and long-term goals and are encouraged to select their own repertoire to practise for their final performances as well as keeping a Practice Log to allow them to monitor their progress. |
|
|
Unit 7 – Music Sequencing |
This Unit enables students to create music using a variety of sources, including loops and software instruments. Students learn how to edit their music using by the application of different processes such as quantisation, looping and note editing, and enhance the the sound by the addition of appropriate plug-in effects such as reverb, delay and distortion. In addition, they learn how to create a final mix which will become a completed audio file. |
|

