Computing and Business
Here you will find information about Computing and Business Studies.
“The only way to great work is to love what you do.”
Steve Jobs
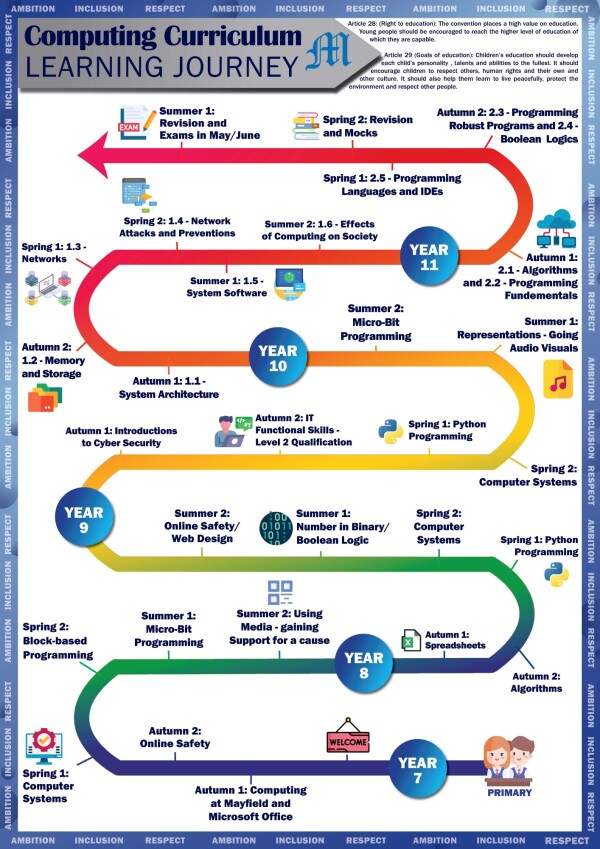
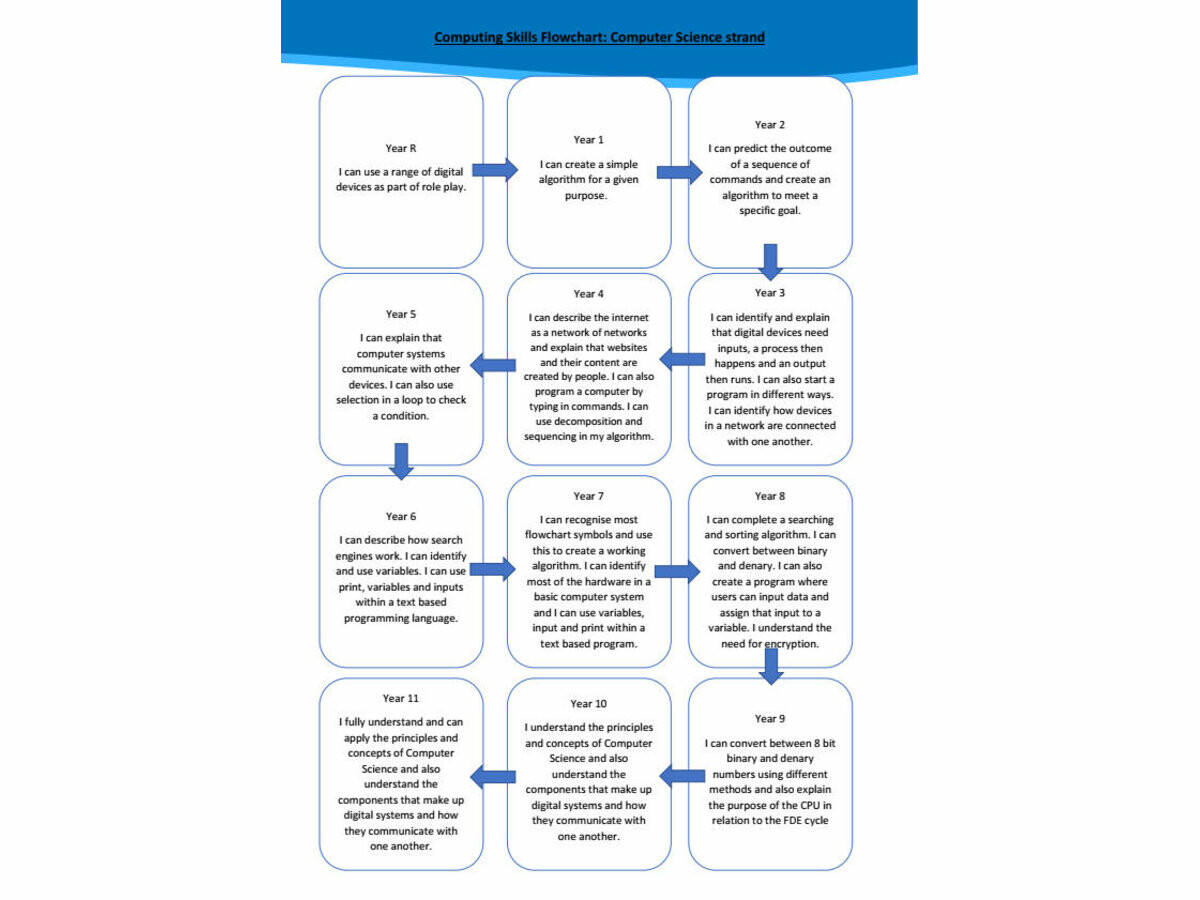
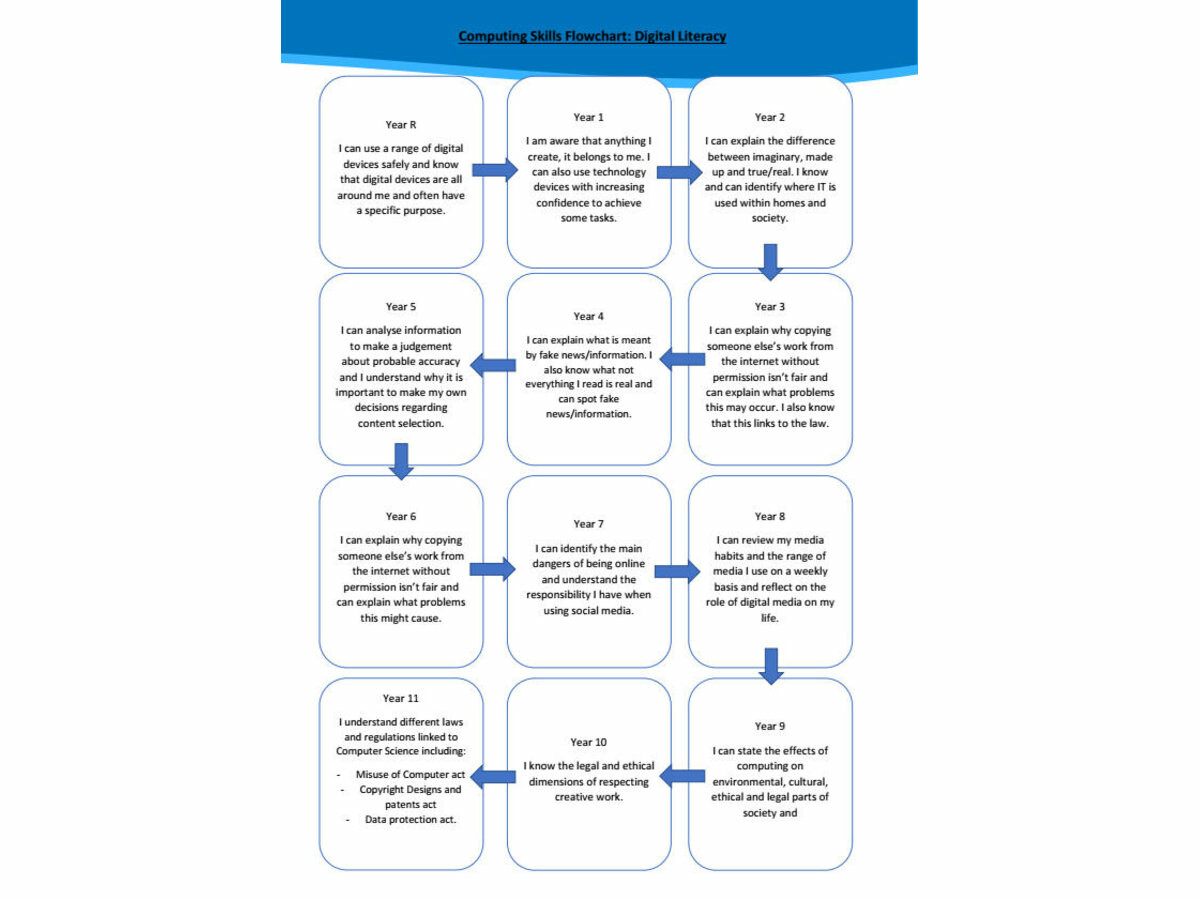
At Mayfield, we understand the importance of Computing and the doors that this subject can open. With this in mind, the curriculum is designed to allow students, to explore potential career pathways. Students are taught a range of skills so that when they come to need a specific key for a specific job, they are equipped with it. Whether it’s a video editor, programmer, network manager or anything else in the industry, the Mayfield Computing curriculum is deliberately designed to cover as many areas of the industry as possible whilst teaching students transferrable life skills which they will continue to develop as they go through the school. We aim to prepare students to become productive, responsible, ethical, creative and compassionate members of the digital world. One key belief of Computing at Mayfield, is the principle of allowing the students to try something new and to make their own mistakes and learn from them.
"It’s fine to celebrate success but it is more important to heed the lessons of failure."
Our goal in Business Studies is to equip our young people with the skills, knowledge, resilience and mindset to thrive in the world of business and make a change for the better. Students can gain a range of skills by engaging in our excellent Enterprise opportunities through their time at Mayfield.
In an ever-changing political world, the study of Business and how businesses are set up, grow and change has never been more important post-pandemic. The way in which businesses of today make, spend, save and use money to trade is critical for moving our local, national and international economy forward. We aim to teach our students about ethics, laws, finances and marketing, with real world case studies and deep rich questions, that allow for a growth mindset. We explore wider Business issues both home and abroad, such as impact of import and exports trade and companies relocating to other countries. Students have the opportunity in Year R-10 to take part in Business enterprise competitions to allow for more practical skills to be developed and prepare themselves for the world of work and post 16 opportunities.
KS4 Qualification Syllabus AQA Business
|
|
Content |
|
3.1 Business in the real world |
|
|
3.1.1 The purpose and nature of businesses |
|
|
Purpose of business
|
|
|
3.1.2 Business ownership |
|
|
3.1.3 Setting business aims and objectives |
• What are business aims and objectives • Purpose of setting objectives • Role of objectives in running a business • Changing objectives • Use of objectives in judging success |
|
3.1.4 Stakeholders |
• Main stakeholders of businesses • Objectives of stakeholders • Impact of business activity on stakeholders • Impact and influence stakeholders have on businesses |
|
3.1.5 Business location |
Factors influencing the location decision of a business |
|
3.1.6 Business planning |
• The purpose of business planning • The main sections within a business plan • Basic financial terms • Basic financial calculations |
|
3.1.7 Expanding a business |
Methods of expansion • Benefits and drawbacks of expansion • Economies of scale • Diseconomies of scale |
|
3.2 Influences on business |
|
|
3.2.1 Technology |
• E-commerce • Digital communication |
|
3.2.3 The economic climate on businesses |
• Interest rates: • how fluctuating interest rates can affect businesses that rely on overdrafts and loans for finance • how fluctuating interest rates can affect consumer and business spending. • Level of employment • Consumer spending |
|
3.2.4 Globalisation |
How UK businesses compete internationally, offering: • better designs • higher quality products at lower prices. Exchange rates |
|
3.2.5 Legislation |
• Employment law • Health and Safety law • Consumer law |
|
3.2.6 Competitive environment |
• Impact on businesses of operating in competitive markets • Uncertainty and risks businesses face |
|
3.3 Business operations |
|
|
3.3.1 Production processes |
Methods of production: • job • flow. Efficiency in production: • lean production • just in time (JIT). |
|
3.3.2 The role of procurement |
Managing stock: • Just in time (JIT) • Just in case (JIC). Factors affecting choice of suppliers including: • price • quality • reliability. |
|
3.3.3 The concept of quality |
Consequences of quality issues Methods of maintaining consistent quality: Total quality management (TQM) Costs and benefits of maintaining quality: • additional sales • image/reputation • higher price • inspection costs • staff training • product recalls • the provision of services. |
|
3.3.4 Good customer services |
Methods of good service: • product knowledge • customer engagement (creating a positive experience for the customer) • post sales services (eg user training, help lines, servicing). Benefits of good customer service, including: • increase in customer satisfaction • customer loyalty • increased spend • profitability. Dangers of poor customer service, including: • dissatisfied customers • poor reputation via word of mouth • reduction in revenue. The ways in which advances in ICT have allowed customer services to develop: • websites • e-commerce • social media. |
|
3.4 Human resources |
|
|
3.4.1 Organisational structures |
• Organisational structures • Appropriateness of organisational structures • Centralisation and decentralisation |
|
3.4.2 Recruitment and selection of employees |
• The need for recruitment • Methods of recruitment and selection of employees • Contracts of employment |
|
3.4.4 Training |
• Importance of training the workforce • Types of training undertaken by businesses |
|
3.5 Marketing |
|
|
3.5.1 Identifying and understanding customers |
The importance of identifying and satisfying customer needs |
|
3.5.2 Segmentation |
Types of segmentation |
|
3.5.3 The purpose and methods of market research |
Purpose of market research Collect information about: • demand • competition • target market. Methods of market research to include primary and secondary: • questionnaires • surveys • interviews • focus groups • internet research • printed press eg newspapers. Use of market research: information that may help decision making |
|
3.5.4 The elements of the marketing mix: price, product, promotion and place (4Ps) |
Pricing methods, including: • price skimming • price penetration • competitive pricing • loss leader • cost-plus. The factors that influence pricing decisions, including: • costs • nature of the market • degree of competition • product life cycle. Product Product differentiation: • unique selling point (USP) • brand image. The product life cycle: • research and development • introduction • growth • maturity • decline • extension strategies: • updating packaging • adding more or different features • changing target market • advertising • price reduction. Product portfolio Promotional methods: • advertising, including: • newspapers • magazines • television • internet • billboards. • PR • sales promotion • point of sales displays • 2 for 1 offers • free gifts • samples • coupons • competitions. • sponsorship • social media. Factors influencing the selection of the promotional mix: • finance available • competitor actions • the nature of the product or service • the nature of the market • target market. Reasons for promotion: • inform/remind customers about the product • create or increase sales • create or change the image of the product • persuade customers to buy the product Place (the different channels of distribution used by businesses): • retailers • wholesalers • telesales E-commerce and m-commerce • Integrated nature of the marketing • Using the marketing mix to inform implement business decisions |
|
3.6 Finance |
|
|
3.6.1 Sources of finance |
• Methods businesses use to raise finance • Appropriateness of sources of finance |
|
3.6.2 Cash flow |
• Importance of cash to businesses • Interpreting cash flow forecasts • Difference between cash and profit |
|
3.6.3 Financial terms and calculations |
• Basic financial terms • Basic financial calculations • Average rate of return • Break-even |
|
3.6.4 Analysing the financial performance of a business |
• Purpose of financial statements • Components of financial statements • Interpretation of data given on financial statements |
Students taking part in enterprise activities, including:
- Made In Portsmouth - year 10's (includes a presentation)
- Faith and Football - year 9's (includes a presentation)
- Fiver challenge - year 4's (includes a presentation)
- Unlock - Three different enterprise days at Portsmouth College and one whole year day at Mayfield (all with different students) (includes a presentation)
- BoE guest speaker - All business students and IGNITE
- Enterprise Week assembly and Dockyard sessions
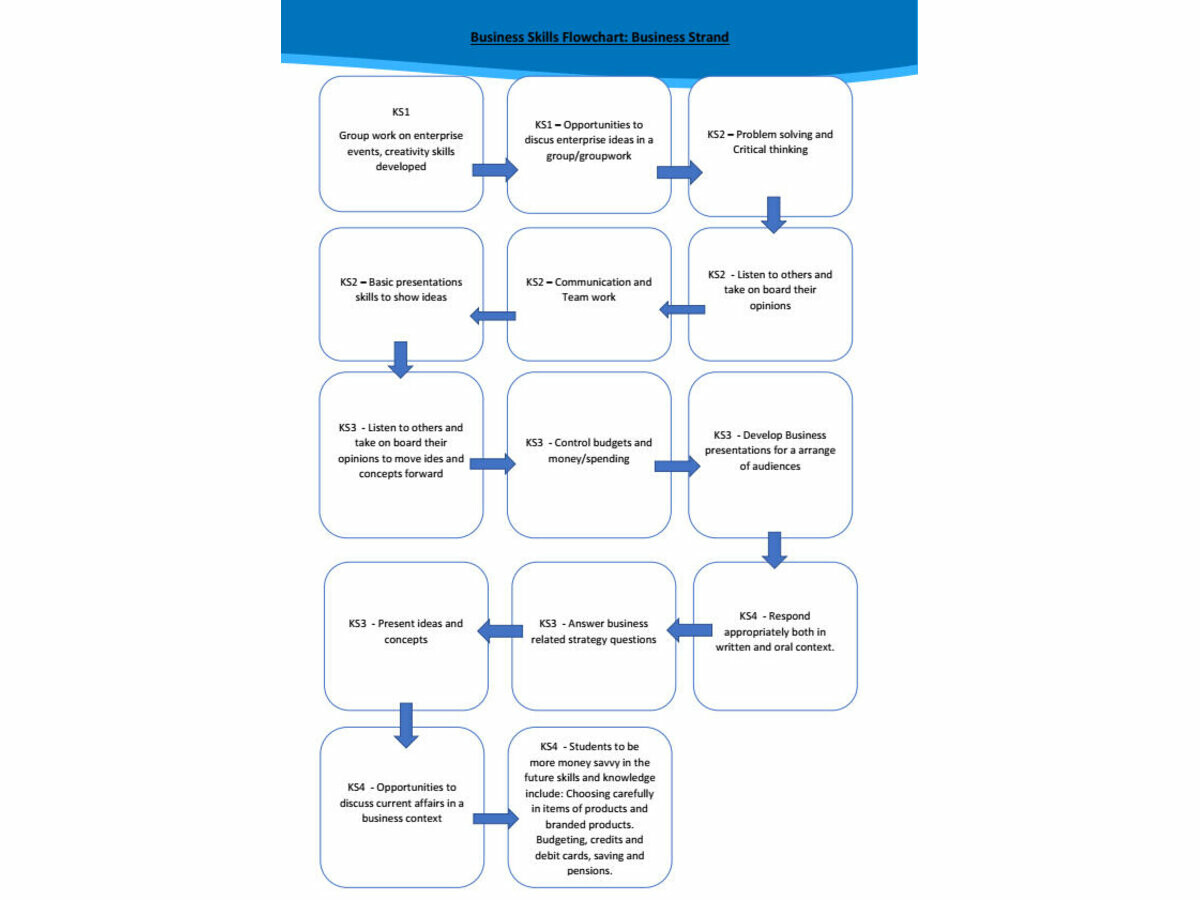
Skills in Business:
- Business presentations
- Using resources well
- Present ideas and concepts
- Listen to others and take on board their opinions
- Respond appropriately both in written and oral context.
- Opportunities to discuss current affairs in a business context
- Students to be more money savvy in the future skills and knowledge include: Choosing carefully in items of products and branded products. Budgeting, credits and debit cards, saving and pensions.